testing voltage drop through a fuse|voltage drop across fuse chart : importing Tracking down a parasitic current draw can be a nightmare — proper testing is essential to find the battery drain. This procedure (and corresponding voltage . bet365 - The world’s favourite online sports betting company. The most comprehensive In .
{plog:ftitle_list}
9 de abr. de 2018 · The idea of the rich international student stereotype is not new. As long as studying internationally has been an option, students all over the world have generalised those who pay that bit extra to study .
Tracking down a parasitic current draw can be a nightmare — proper testing is essential to find the battery drain. This procedure (and corresponding voltage .
This test will show you how to quickly pinpoint the source of the draw using voltage drop across fuses. This method is fast and efficient in comparison to monitoring current and removing. Step 3: Set the Multimeter to the Correct Mode. Before testing, you need to set the multimeter to the correct mode: Continuity Mode: Ideal for a quick check, as the multimeter will . 1 Blade-type fuses have test points on top, a good place to meter the voltage in a circuit. Try this: Meter both test points on the millivolt range, . Using a DMM to locate which circuit is causing a parasitic battery drain by measuring the voltage drop across a fuse!
Method #2 Use voltage drop testing for parasitic battery drain In this method, you use a multimeter to check for voltage drop across each fuse. See the testing routine below.“Voltage dropping” a circuit will tell you when the cir-cuit is too restricted to operate a component (motor, relay, light bulb, etc.) or operate it correctly. If the circuit is restricted, repair it and .
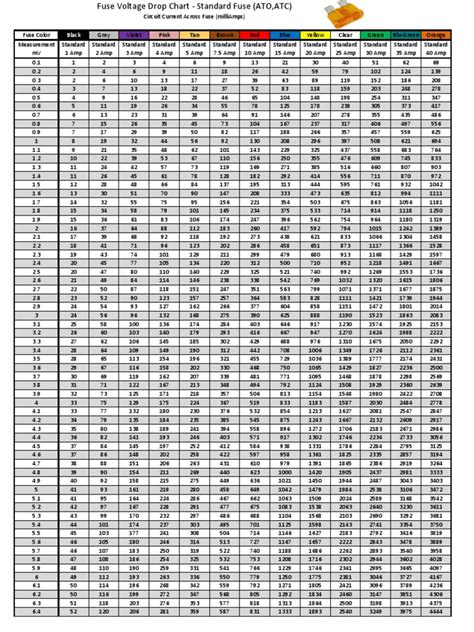
voltage drop across fuse chart
Voltage drop testing is done by using a DMM to monitor actual voltage/amperage on a particular circuit, group of circuits, component, or electrical system (windshield wipers, cruise control, charging system, etc.).The snag with smaller oscilloscope amp clamps is that the hole through the jaws are usually too small for the negative ground cable. . current is flowing through a piece of wire or a fuse, the voltage will drop ever so slightly. . test in the .%PDF-1.4 %âãÏÓ 854 0 obj > endobj xref 854 18 0000000016 00000 n 0000001105 00000 n 0000001380 00000 n 0000001686 00000 n 0000002205 00000 n 0000002242 00000 n 0000002471 00000 n 0000002549 00000 n 0000002999 00000 n 0000003374 00000 n 0000003714 00000 n 0000004050 00000 n 0000004405 00000 n 0000004800 00000 n .
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like All of the following are true concerning electrical shorts, EXCEPT: a. A short can add a parallel leg to the circuit, which lowers the entire circuit's resistance. b. A short can result in a blown fuse. c. A short decreases amperage in the circuit. d. A short bypasses the circuit's intended path., A "blown" fusible link . This low resistance means that the voltage drop across the fuse will be very small. Why, then, do fuses have a voltage rating? It’s true that fuses see small voltage during normal operation, but the voltage rating is not relevant to normal operation. Rather, the voltage rating tells you what the fuse can endure after it has tripped. A blown . Here are the results of the volt drop test across the 25-amp rear wiper fuse. The volt meter shows 0.3 mA of volt drop. This fuse is showing 0.6 amp of current. A less-intrusive way to find the current flow is performing a voltage drop test across each fuse with your DVOM set to the milliamp voltage scale. Across the fuse, 0V indicates a good fuse and Source voltage indicates a bad fuse. From fuse to ground (or return), Voltage on the source side and voltage on the load side indicates a good fuse. Voltage on the source side and no voltage on the load side indicates a .
%PDF-1.6 %âãÏÓ 7632 0 obj > endobj 7647 0 obj >/Filter/FlateDecode/ID[2557EF52E832834F8480CADC7430BA6E>7A2EBA31C63D88449810E086A080ACB0>]/Index[7632 20]/Info 7631 .
1 Blade-type fuses have test points on top, a good place to meter the voltage in a circuit. Try this: Meter both test points on the millivolt range, and read the voltage drop across the fuse. Voltage drop testing allows the technician to monitor voltage loss in a circuit. Voltage drop should be checked with the circuit loaded and a fully-charged b.age. After approximately 10 minutes, amperage should drop to a stable value less than 20 mA. • If amperage is 40mA or higher, follow the fuse voltage drop test to identify the fuse(s) with an ongoing draw. • Measure all fuses and record voltage drop, fuse location, type and rating. 6. After all fuses are tested, identify the suspect .Discover the step-by-step guide on how to test a fuse with a multimeter, an essential skill for every household. . such as measuring voltage, current, and resistance. . This means that the current can flow through the fuse without any obstruction. On the other hand, if the fuse is blown or faulty, the multimeter will show an infinite .
We measure the voltage drop across each of the fuses. That's right, even a fuse has some resistance when heated due to current flow across it. This means the fuse that has current flowing will have a measurable voltage drop across it. Simply set your DMM to the millivolt scale and place the test leads across the fuse as shown in Figure 1. To test the condition of the contacts (excessive resistance from pitting that causes an excessive voltage drop) this voltage drop test should be done: Here we have a fuse located on the “ground” side of the relay switch. This is a common circuit arrangement you will see.
stabilized voltage drop across the fuse, with current equal to the nominal rated current flowing through it. Resistance data on all Littelfuse products are available on request. Fuses can be supplied to specified controlled resistance tolerances at additional cost. SOLDERING RECOMMENDATIONS: Since most fuse3. Voltage Test. When it comes to testing fuses, checking the voltage is just as important as testing for continuity and resistance. While continuity and resistance tests determine if there’s a clear path for current to flow, a voltage test checks . There’s no volt drop across the fuse. But when I turn the radio on, the multimeter reads 3.4 millivolts. That tells us that we have some current going through the circuit. Measuring voltage drop across the fuse is as simple as . Select a high range on the dial for the test. Choose a range according to the regular voltage of the device you wish to test. The voltage is printed on some devices and included in the user manual on others. To get an accurate result while protecting the multimeter from damage, set the dial at the next highest voltage setting available.
The clearing I 2 t is proportional to the total energy let through by the fuse when clearing a fault. The energy is mainly dependent on current and time for fuses as well as the available fault level and system voltage. . Once current is applied, resistance and voltage drop of a fuse will constantly grow with the rise of its operating .
Voltage drop testing is being discussed. Technician A connects the red voltmeter lead to the most positive side of the circuit being tested and the black lead to the most negative side or part of the circuit being tested. Technician B says the test must be conducted with the circuit operating with normal amounts of current. Who is correct? a. A . Check The Fuse Checking The Voltage Level Of A Fuse In A Car With A DMM. Place the tips of both leads on the fuse metal end caps and look at the display of the voltmeter. You will see zero or near-zero voltage, which means the fuse is good. If the volt potential across the fuse is the full supply voltage, it means the fuse is bad and needs .
Just to clarify I am not receiving the 12-13v from pin 30 to 87 with the key on. I have swapped multiple relays inside 6 to be exact. I have also tested 4 relays using a power supply and adding power across pins 86 and 30 and took readings of the voltage on just the relay itself and they were functioning properly. Place the meter leads on either side of the fuse. If there is little to no voltage indicated, the fuse is good. However, if there’s a difference in voltage (typically the full supply voltage), then the fuse is bad. Step 2: Replace the fuse. It’s best practice to replace the bad fuse with one that’s identically spec’d.
To calculate the voltage drop across a resistor using Ohm's law, proceed as follows: Find out the resistance of the resistor. Measure the current through the resistor using an ammeter. Multiply the current by the resistance to get the voltage drop using Ohm's law.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like DVOMs and automotive test lights can be used to _______., Tech A states that DMMs come in a variety of layouts and qualities. Tech B states that DMMs and test leads also should have a CAT rating listed on the front. Who is correct?, DMMs of average quality or better are "fused," meaning that one or .
checked by means of a millivolt drop test. A known current is placed through the fuse. Since its resistance is known, it will produce a millivolt drop across the fuse. This voltage drop is measured and compared to the standard. Any fuse that proves discontinuous or otherwise out of tolerance is rejected. The millivolt drop test accomplishes two .97-20-01TT Voltage Drop Testing Procedures Release date: 4/30/2020 1 Condition ATTENTION: . (0.1 volts) goes through the meter, giving a voltage drop reading of 0.1 volts. Meter #4 4.0 volt drop across the damaged wire. The wire has high resistance at the fault point, allowing only 7.9 volts through . Voltage Drop testing is simply running the test lead of your meter the entire route --- from the battery to the fuseblock to the switch to the connector to the wire to the motor --- and physically MEASURING, "Hey, I've 11.0 volts one one side of the window switch but only 10.5 on the other side WHEN I PRESS IT!"
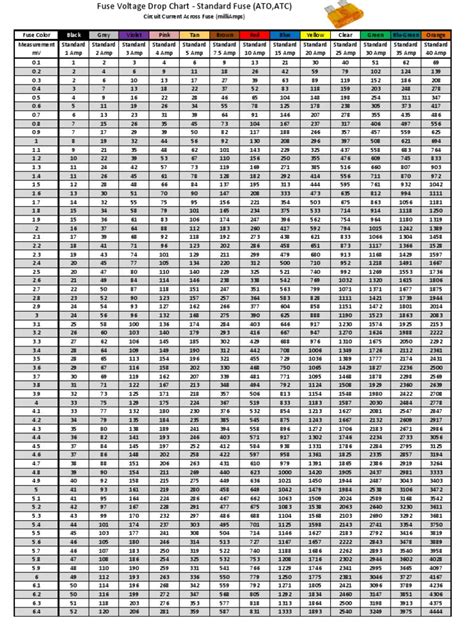
printable fuse voltage drop chart
O melhor de mim Aqui👇. Telegram vip
testing voltage drop through a fuse|voltage drop across fuse chart